Why You Should Think Twice Before Using PDMS in Microfluidic
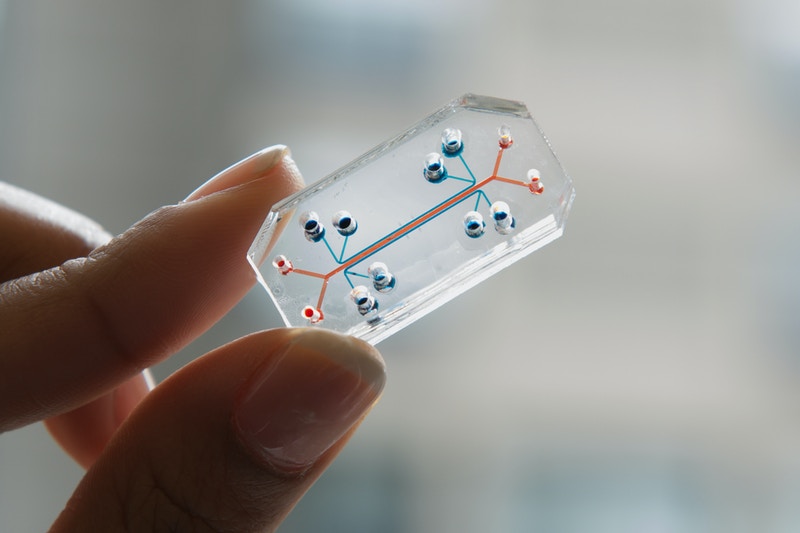
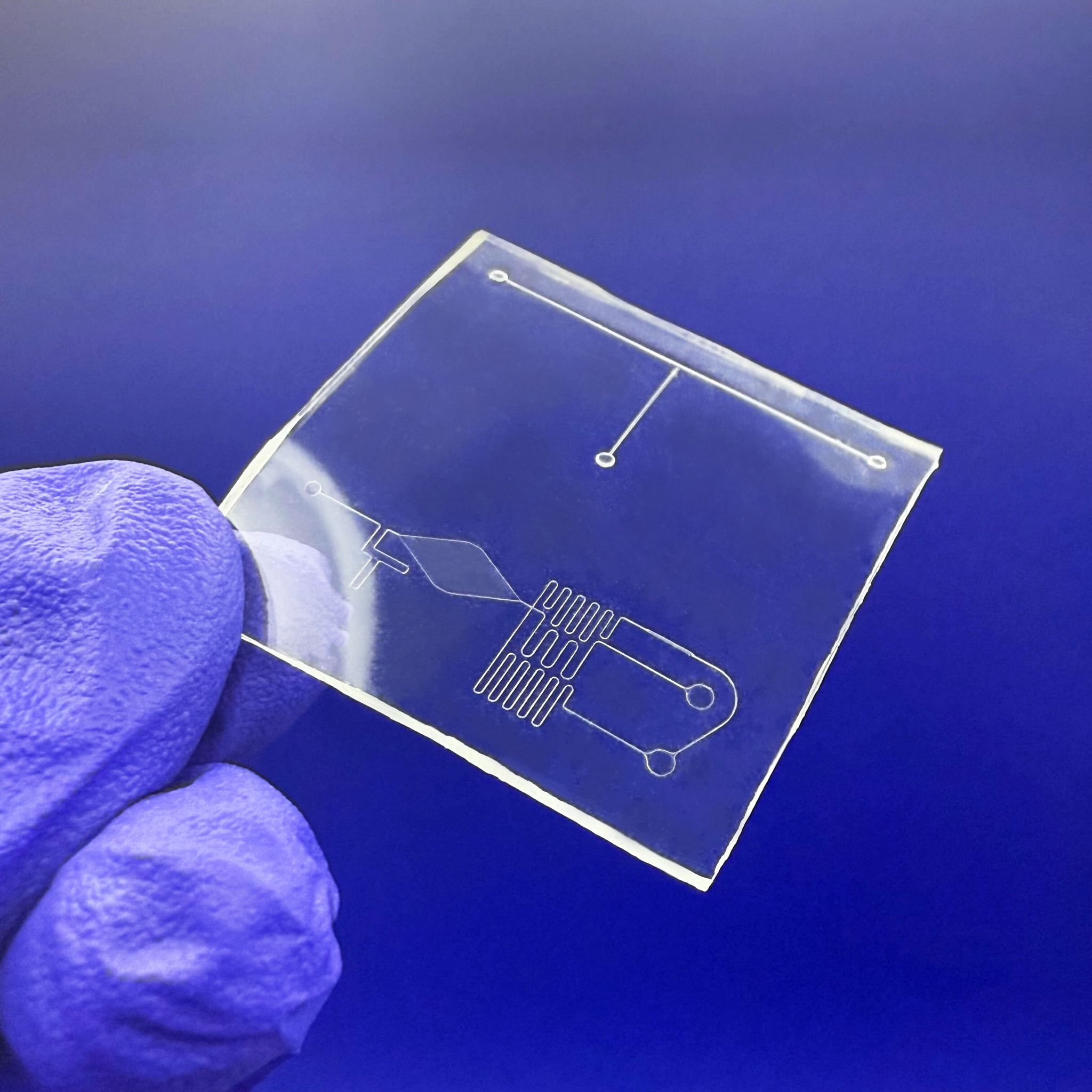
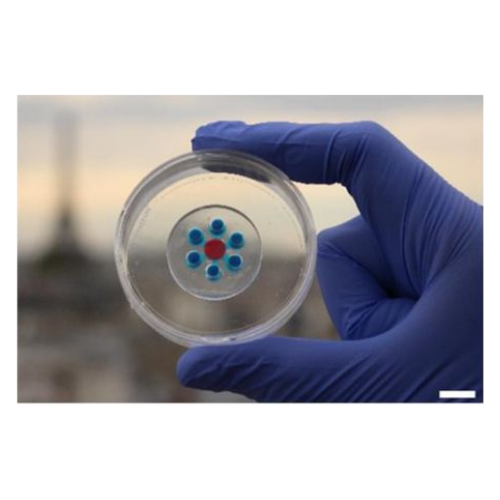
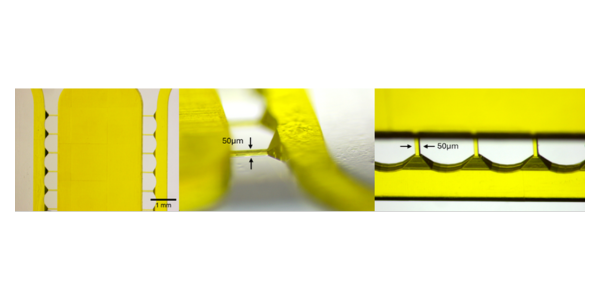
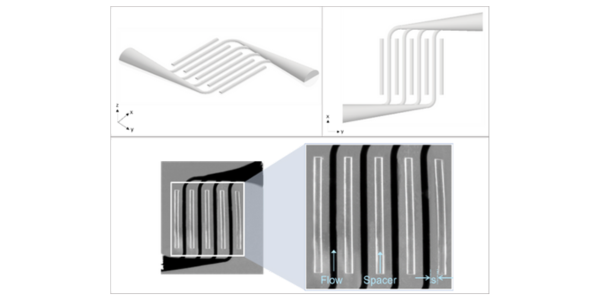
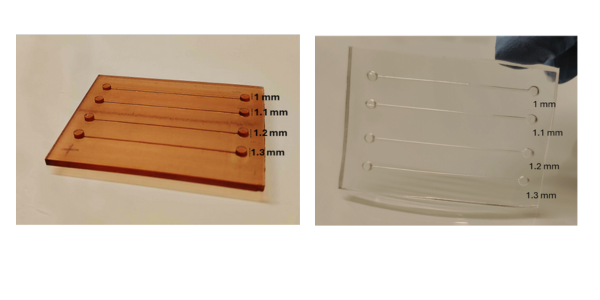
Why You Should Think Twice Before Using PDMS in Microfluidics What is PDMS and Why It’s Popular PDMS (Polydimethylsiloxane) has been the go-to material in academic microfluidics. Its low cost, optical clarity, and ease of prototyping via soft lithography made it the standard in university labs. But times have changed. In industrial, diagnostic, and even […]
Why You Should Think Twice Before Using PDMS in Microfluidic Read More »