The Alternative to PDMS
Flexdym™ is a thermoplastic elastomer engineered for microfluidics that solves the critical limitations of PDMS, allowing you to prototype quickly, bond easily, and scale without compromise.
From Micro to Nano-Sized Structures
DEVICE REPLICATION
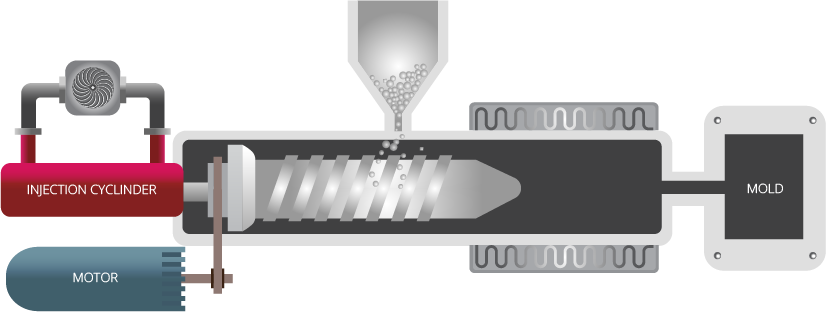
Flexdym™ microfluidic chips are molded and replicated via hot embossing, which allows the replication of structures at higher levels of accuracy and precision than soft lithography.
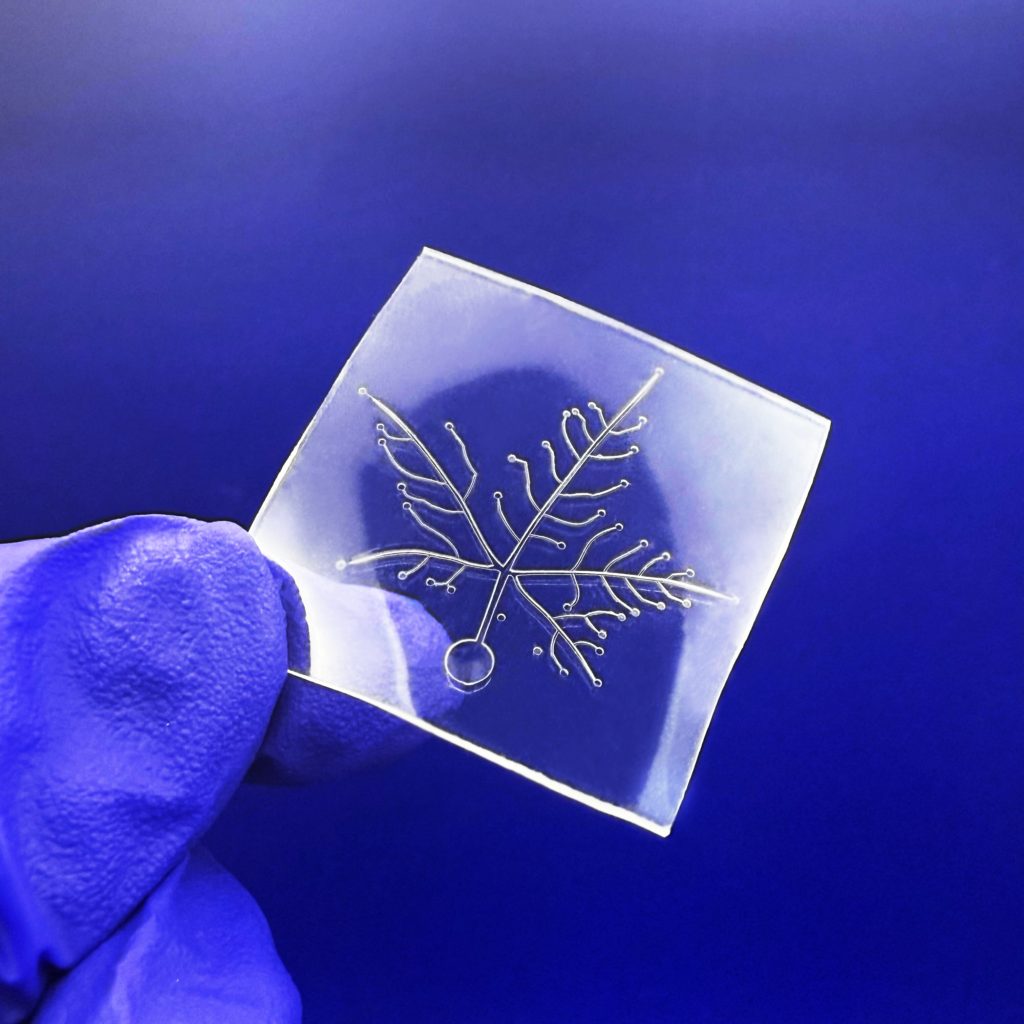
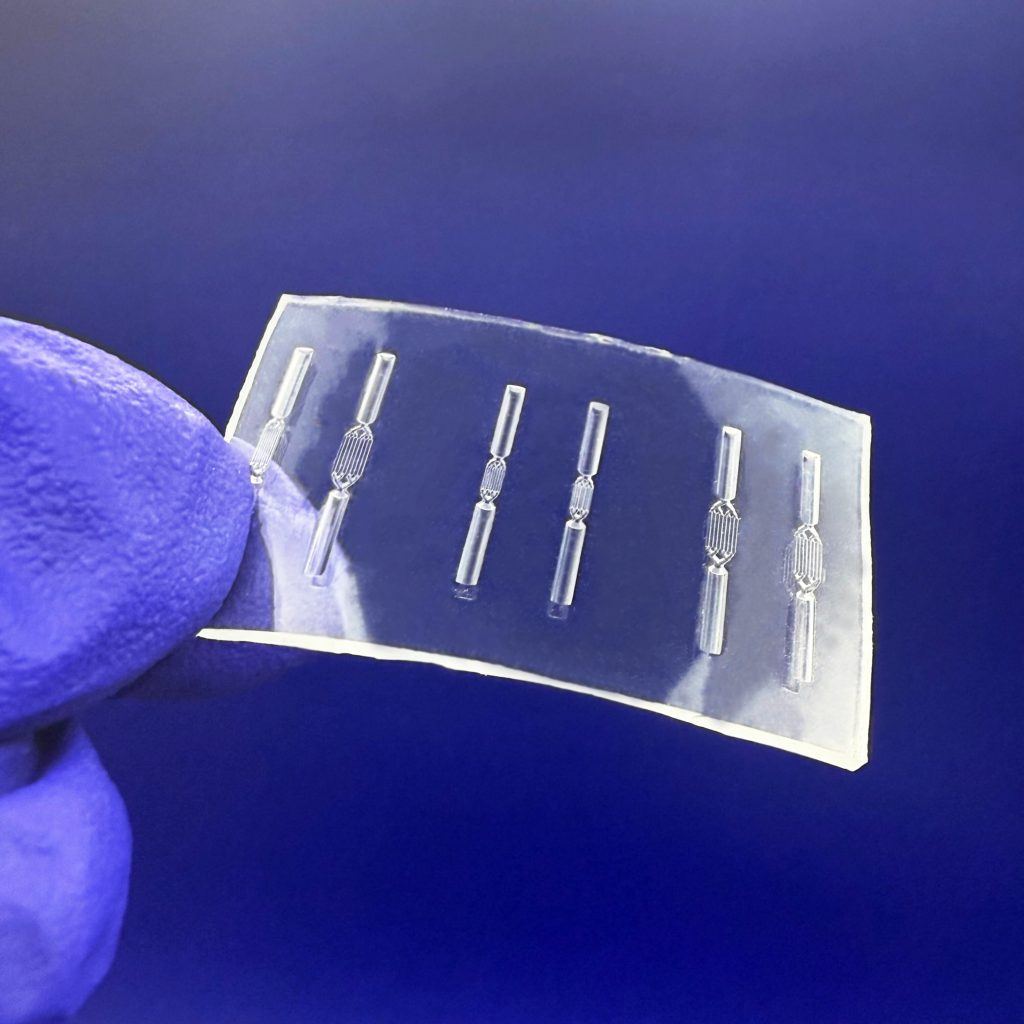
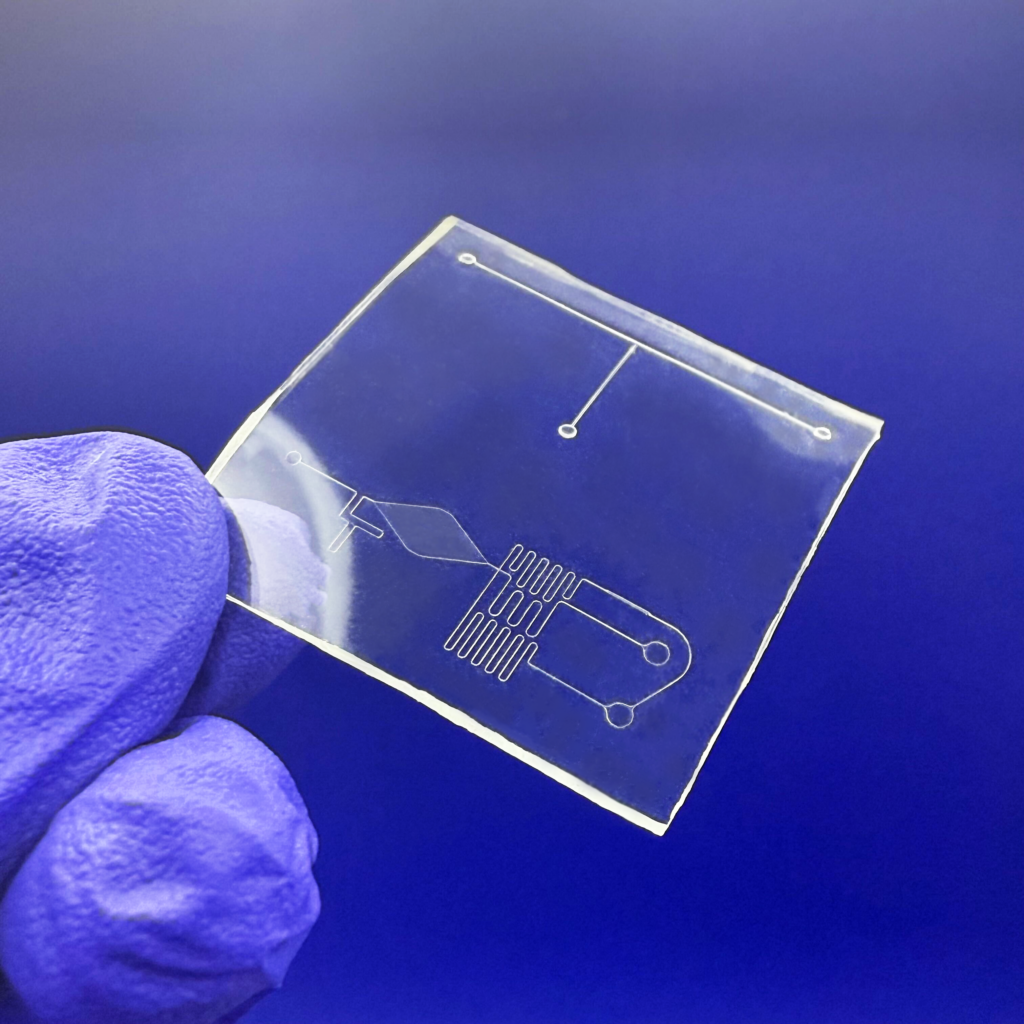

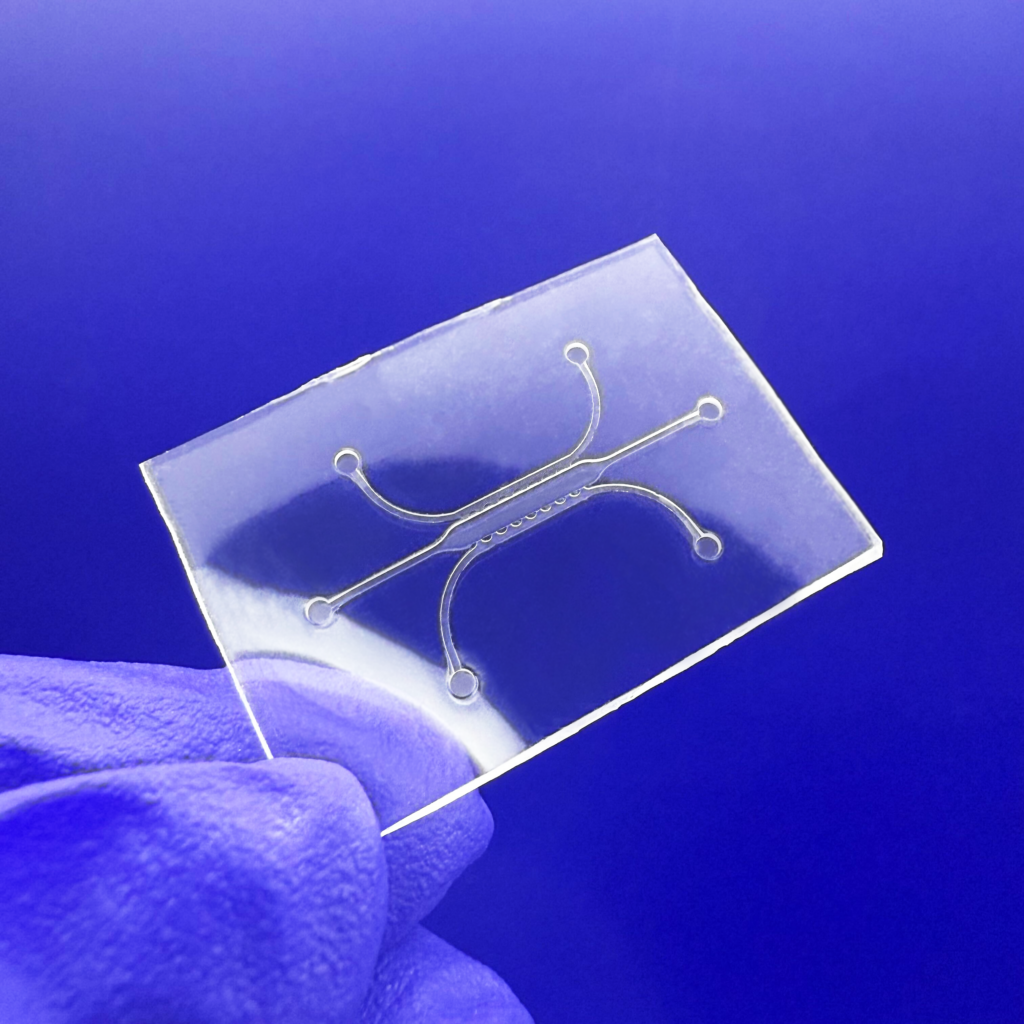
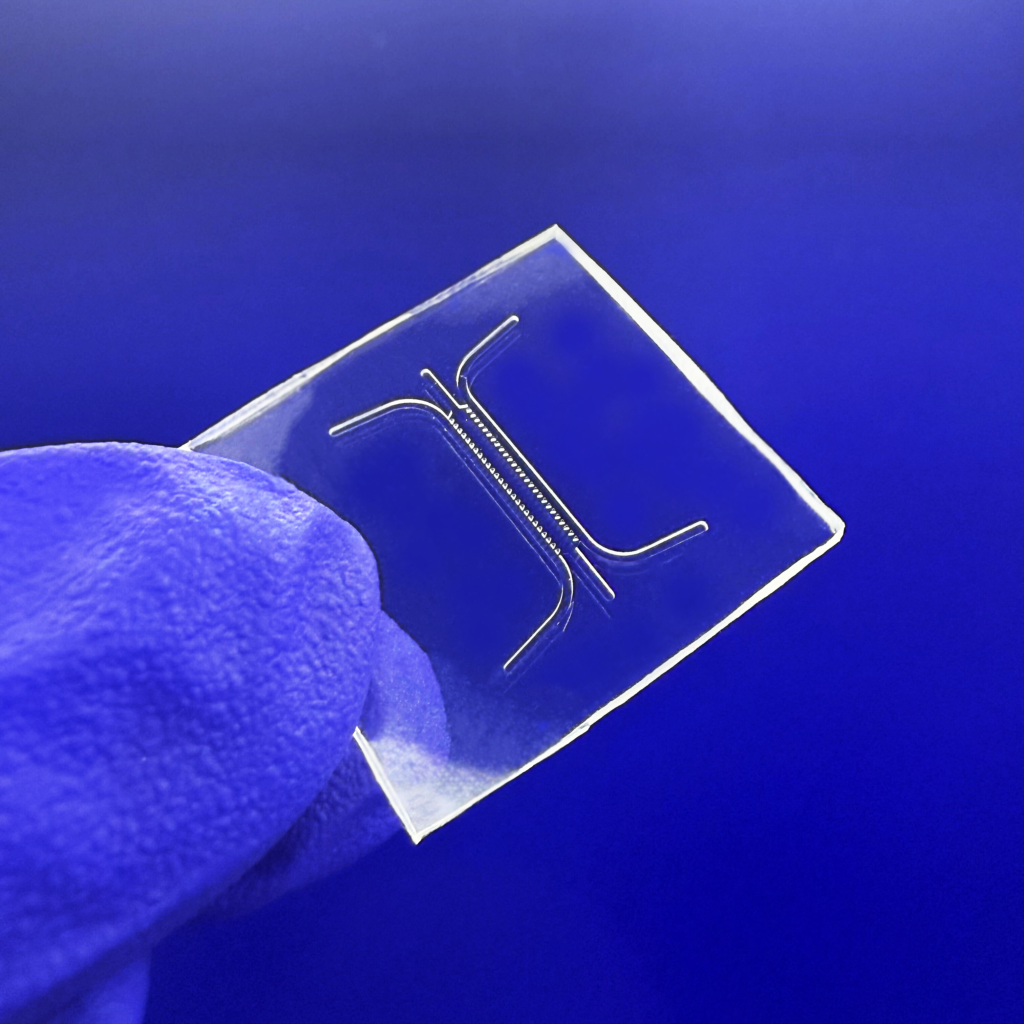
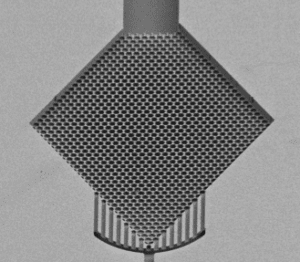
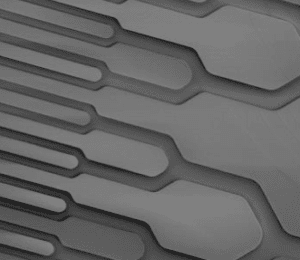
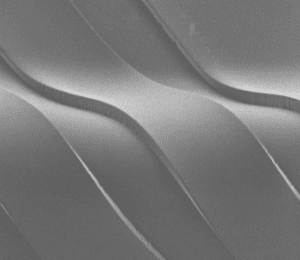

Problems: The Limitations of PDMS in Microfluidics
Solution: Flexdym™
- High small molecule adsorption → skewed bioassay results
- Oligomer leaching → compromised cell cultures and surface chemistry
- Non-scalable → not suitable for industrial manufacturing
- Requires plasma bonding → adds complexity and cost
- Low adsorption of small molecules → Preserve sample integrity and signal fidelity
- No oligomer leaching → Maintain clean microenvironments for sensitive biological experiments
- Room-temperature reversible bonding → No plasma or cleanroom needed
- Available in Sheets, Rolls & Pellets → Designed for fast prototyping and mass production
- Biocompatible & ISO 10993 certified → Ready for life science applications
Microfluidic Expert Interview




























































































Flexdym™ Features
Flexdym™ embodies specific core values critical for advanced microfluidics: its inherent Biocompatibility, exceptional Versatility in Fabrication, and remarkable Scalability. These intrinsic properties are fundamental to its innovative application.
- Biocompatible & ISO 10993 Certified : For reliable results in biological and clinical research.
- Reversible Bonding at Room Temperature : Forget plasma. Just press and go.
- Reusable : Flexdym is remoldable and recyclable ideal for sustainable workflows.
- Low Adsorption of Small Molecules : Ensure accurate biological assays, Flexdym™ keeps your compounds where they belong.
- No Leaching of Oligomers : Unlike PDMS, Flexdym does not release uncrosslinked materials that can interfere with sensitive experiments.
- Available in Sheets, Rolls & Pellets : Whether you're prototyping or scaling to industrial production, Flexdym™ grows with you.
Key Features
- Room Temperature Bonding (RTB): Enables fast, equipment-free assembly.
- No Deformation or Warping: Maintains microchannel integrity during bonding.
- Reversible & Irreversible Bonding throught different methods, up to 4 bar.
- Substrate Compatibility: Bonds to Flexdym™, Glass, COC, PMMA, PS, even when untreated.
- Cost-Effective & Scalable: Reduces fabrication cost and is suitable for prototyping and mass production.
Ideal for
- Microfluidic prototyping
- Diagnostic and lab-on-chip devices
- Injection-molded components
- Biological and tissue engineering applications
We have conducted gas permeability tests for 2 mm of Flexdym at 23°C, 50% RH. Subsequently, these results, combined with those of other Flexdym™ users, show a range of 40 to 70-fold lower gas permeability for Flexdym™ compared to PDMS. Nevertheless, cell culture remains a top application of Flexdym™. For instance, for published results, contact us.

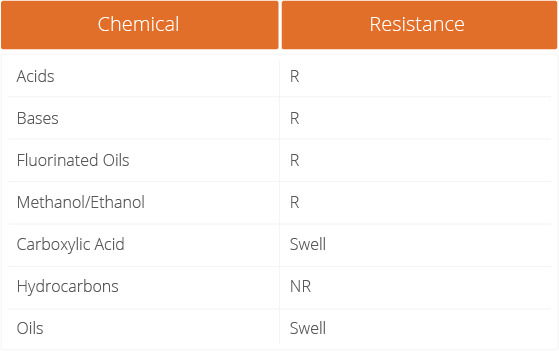
Much like PDMS and other thermoplastic materials used in microfluidic device fabrication, Flexdym™ is resistant to commonly used solvents such as acids and bases, as well as methanol/ethanol. Furthermore, it is resistant to fluorinated oils, commonly used in droplet-based microfluidic applications. However, like these other materials, results show it swells in the presence of carboxylic acid and other oils. Indeed, it may be important to note, it is not resistant to hydrocarbons. To that end, to find out more about Flexdym™ material chemistry, read our news article.
Flexdym™ combines properties of thermoplastics and elastomers. This explains it’s elasticity (Young Modulus of 1.15 MPa) and simultaneous ability to be hot embossed.

Flexdym SHEETS Starter Pack
The starter pack is the perfect format for first-time Flexdym™ users to test the material for their application. Moreover, within one starter pack, different thicknesses can be mixed, making the selection process easier for you.

Flexdym Rolls
Following initial testing, the Flexdym Rolls offer a more cost-effective format for users. Furthermore, they are compatible with roll-to-roll embossing methods for mass production.

Flexdym Pellets
For experienced users, the Flexdym™ Pellets are ideal for those who have developed a marketable product using this technology. Subsequently, they are suitable for beginning mass production or 3D printing with our Flexdym pellets.
Easy Steps for Flexdym™ Microfluidic Chips
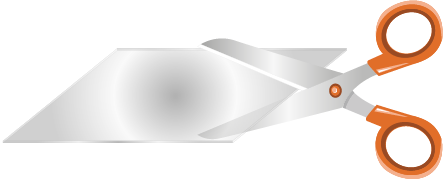
01
Cut it
Cut the protected Flexdym™ sheet to the required dimensions: the material is ready to be molded.

02
Press it
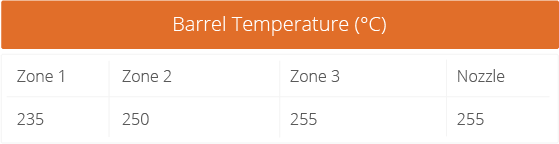
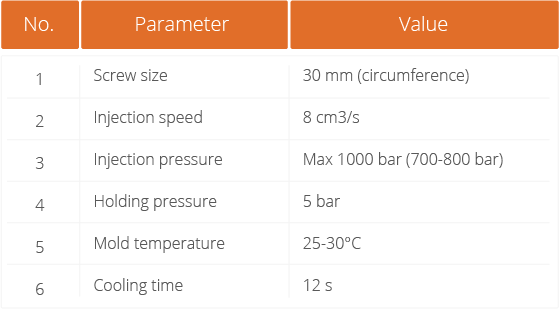
Remove the protective film from one side of the sheet. Place the exposed surface in direct contact with the mold. Apply controlled heat (e.g., 110–165 °C) and pressure to transfer the desired microstructure.
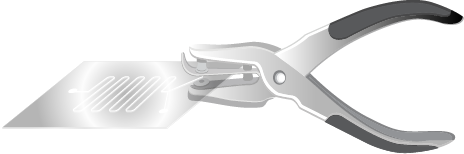
03
Punch Inlets
Punch inlet and outlet holes at the designated positions using a puncher of appropriate diameter.

04
Place it
Bond the molded Flexdym™ layer with the chosen substrate (e.g., glass, PMMA, COC). Your Flexdym™ device is now ready for use.
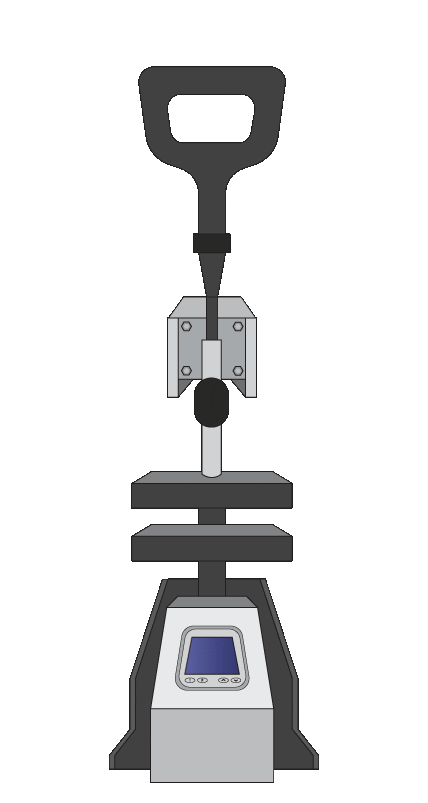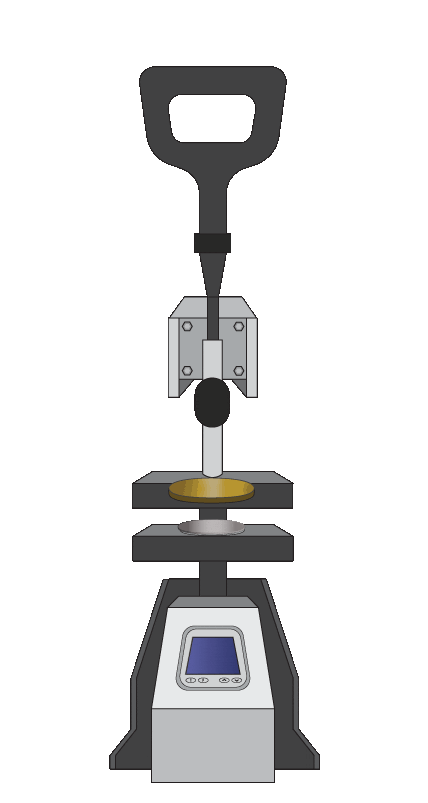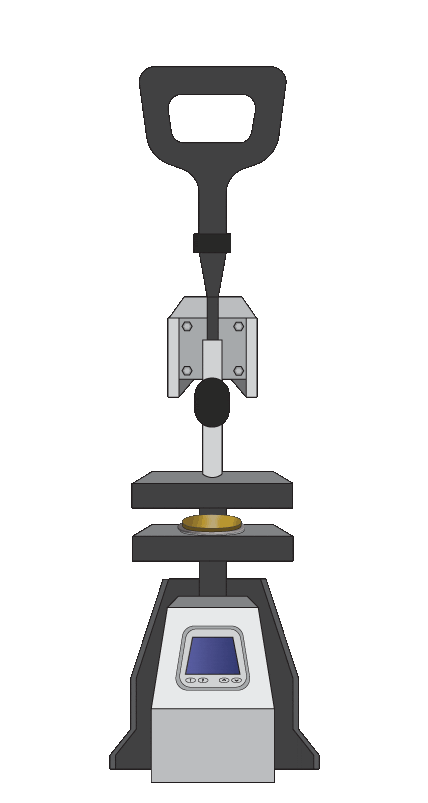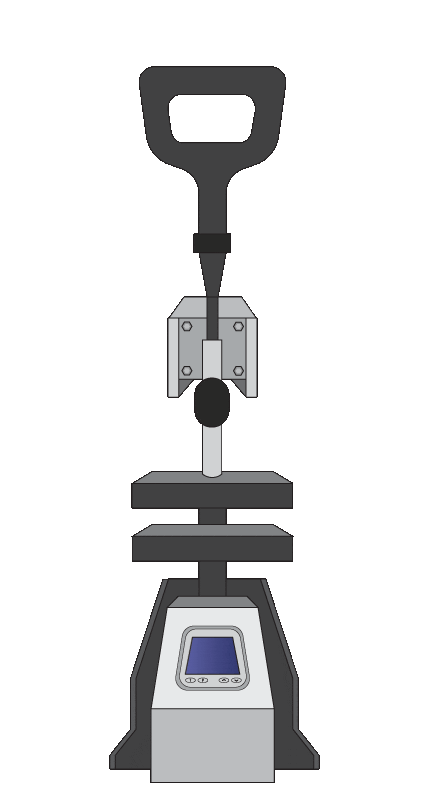
Microfabrication Process with Flexdym™
- Optimized for Flexdym™ molding in only 1-2 minutes!
- Compact & User-friendly design that requires little to no training.
- Dramatically cheaper than most standard clean room equipment. This small investment is an opportunity for you to begin exploring microfluidics.
Classic Hot Press
- Not optimized for Flexdym™ molding, therefore longer molding time.
- Less easy-to-use alternative for the Sublym.
- Slightly more expensive than the Sublym100, but a standard piece of equipment which is generally installed in fabrication facilities.
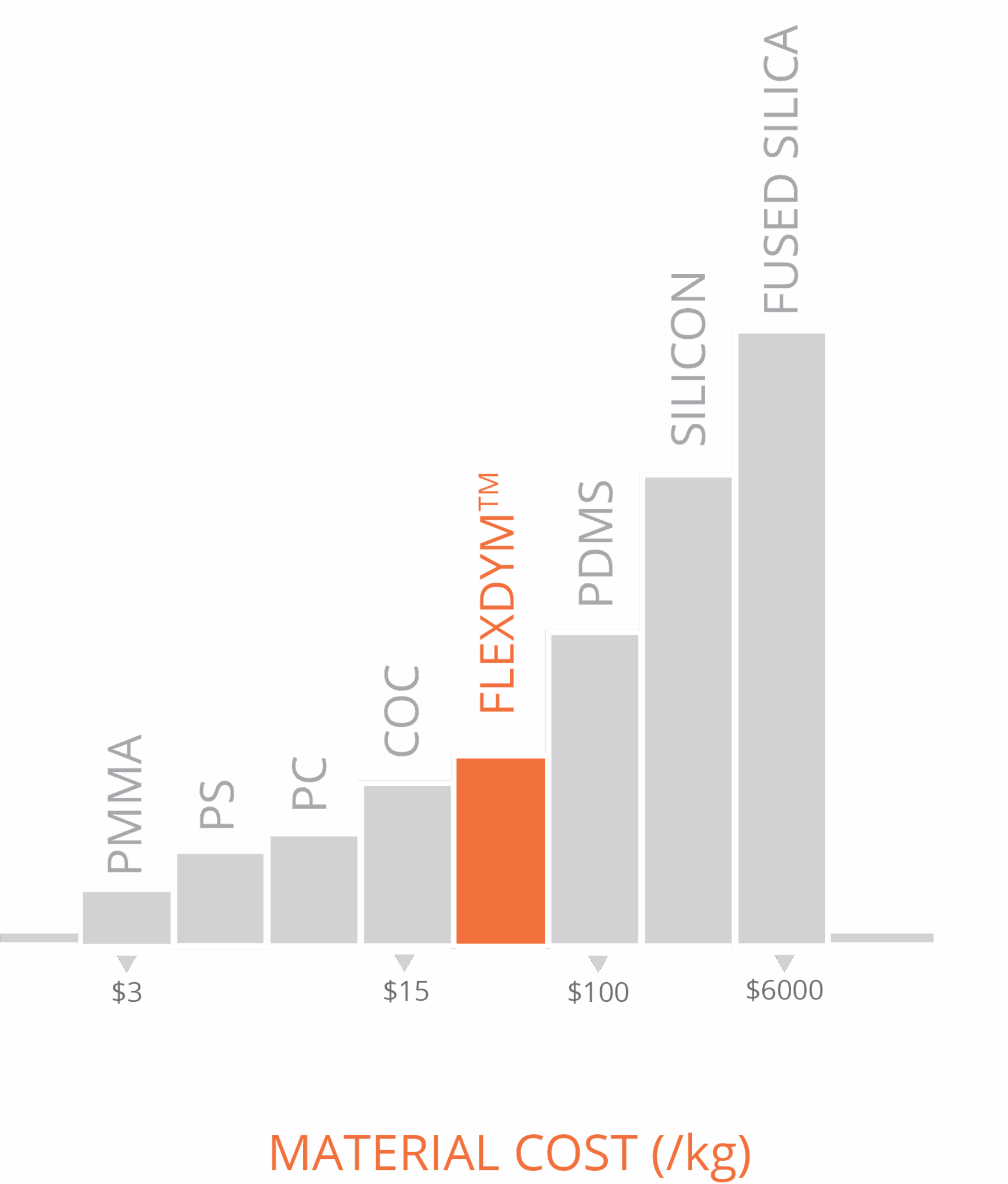
Flexdym Pricing
Eden Tech has optimized Flexdym™’s pricing to be comparable to other widely used materials in microfluidics, with added advantages:
- Biocompatible
- Transparent
- Scalable
- User-Friendly
Application Notes, Case Studies & Top Flexdym™ Applications
Flexdym™ for Cell Study Devices
- Certified Biocompatible ISO 10993 parts 4, 5, 6, 10 & 11 AND USP Class VI.
- Good cell adhesion & proliferation over long time periods.
- Bonding to PS, glass and other commonly used cell culture materials.
- Good bonding strength up to several bars, withstands 37°C humidity conditions.
- Stable hydrophilicity post plasma treatment.
- Gas permeable, but low sorption of small molecules.
Top Flexdym Applications
- 2017 - Thermoplastic elastomer with advanced hydrophilization and bonding performances for rapid (30 s) and easy molding of microfluidic devices
- 2018 - Soft Thermoplastic Elastomer for Easy and Rapid Spin-Coating Fabrication of Microfluidic Devices with High Hydrophilization and Bonding Performances
- 2019 - Harnessing Nonlinearity and Asymmetry for Built-in Control in Mechanical and Fluid Systems
- 2019 - Microfluidics: Innovations in Materials and Their Fabrication and Functionalization
- 2019 - Development of fast and simple fabrication processes for paper-based microfluidics and alternative polymers to PDMS
- 2020 - Rapid Fabrication of Membrane-Integrated Thermoplastic Elastomer Microfluidic Devices
- 2021 - Facile engineering and interfacing of styrenic block copolymers devices for low-cost, multipurpose microfluidic applications
- 2021 - Estudi de la fabricació de canals microfluídics en làmines polimèriques i la seva unió mitjançant hot embossing i processos d’unió tèrmica
- 2022 - Complete fabrication station of scalable microfluidic devices for sensing applications
- 2022 - Engineering a sustainable future for point-of-care diagnostics and single-use microfluidic devices
- 2024 - Low-cost, versatile, and highly reproducible microfabrication pipeline to generate 3D-printed customised cell culture devices with complex designs
- 2017 - Insights on Polymers for Microfluidics Applied to Biomedical Applications
- 2018 - Desarrollo de sistemas microfluídicos en la multiescala para el cultivo celular y tisular
- 2019 - A methodology to develop a vascular geometry for in vitro cell culture using additive manufacturing
- 2021 - Cultivating Multidisciplinarity: Manufacturing and Sensing Challenges in Cultured Meat Production